Hair Loss
Medical Dermatology
Alopecia is a word used to describe any kind of hair loss. There are numerous types of hair loss and treatment depends on its cause.
Alopecia (Hair Loss)
Alopecia is a word used to describe any kind of hair loss. There are numerous types of hair loss and treatment depends on its cause. Hair loss can be very cosmetically concerning though it can be very difficult to distinguish between the many kinds. Speak to your dermatologist if you are experiencing hair loss to find out what kind it is and what treatments are available.
Androgenic Alopecia
Androgenic Alopecia, also known as male pattern baldness, is the most common form of hair loss and can affect women as well as men. Its cause is not fully understood although it is known that androgenic hormones such as testosterone play a role – testosterone stimulates hair growth – men and women with early onset androgenic alopecia have lower than normal androgen levels. However, with age these same hormones begin to inhibit hair growth on the crown and frontal scalp while continuing to stimulate it elsewhere. This process does not occur in everyone, however, so genetics must play a role. This mix of imbalanced androgen levels, age, and genetics results in hair follicles gradually shrinking and eventually becoming dormant.
The most effective treatments for androgenic alopecia involve the use of minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia and Proscar). Hair transplantation procedures work very well to create the appearance of normal hair. There exist a multitude of other proposed treatments by both medical professional and others such as dietary supplements, vitamins, and laser/light treatments. Most of these other treatments are either new and unproven (such as laser/light treatments) or show little to no effectiveness (such as dietary supplements and vitamins). If you believe you have androgenic alopecia consult your dermatologist to explore your treatment options.
Effluvium
Effluvium, a word that means “outflow”, describes a type of hair loss caused by a disruption in the normal cycle of hair growth. Hair follicles follow a pattern of hair growth (typically 1-2 years) followed by a period of dormancy in which the hair fiber falls out and no hair is produced (typically 1-2 months). In a normal scalp the vast majority of hair follicles are in the growth phase and a consistent level of hair is maintained. However, when an abnormally large portion of hair follicles enter the resting state the result is temporary thinning of the hair known as telogen effluvium.
This form of hair loss is typically triggered by a major event that “shocks” the hair follicles into a resting state. Giving birth, a car crash, surgery, reaction to medication, other diseases, and anything that causes extreme stress can all result in telogen effluvium. Hair loss is seen 1-2 months following the event and can persist for many months until the hair follicles reactivate. Most cases of telogen effluvium require no treatment as the hair will begin to regrow naturally. In cases where hair loss is persistent, consulting with a doctor can help isolate the cause of telogen effluvium.
A similar kind of hair loss, known as anagen effluvium, is a reaction to a toxin such as rat poison or cytostatic cancer drugs. These chemicals inhibit rapid cell proliferation – a necessary component of hair growth. This type of effluvium sets on very rapidly but resolves just as rapidly once the chemical causing it is discontinued.
Alopecia Areata
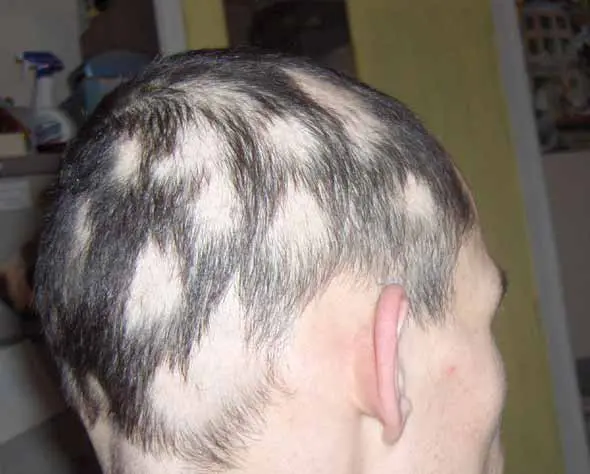
Alopecia areata is a poorly understood form of hair loss that is caused when the body’s immune system incorrectly recognizes hair follicles as a threat to the body and attacks them, resulting in patches of hair loss. It is unknown what triggers the immune system in these cases.
Alopecia Areata
In most individuals alopecia areata manifests as a round patch of hair loss on the scalp, though in extreme cases it can affect the entire scalp or other areas of the body. Almost all cases of alopecia areata resolve within two years with or without treatment. Most treatments for this condition involve topical steroid or steroid injections, though for some individuals no treatment is effective.
Cicatricial Alopecia (Scarring Alopecia)
Scarring alopecia describes hair loss due to the creation of scar tissue in areas of normal hair growth. There are many kinds of diseases that can create scar tissue such as folliculitis decalvans, dissecting cellulitis, or even lupus erythematosus. Whatever the cause, the scarring results in the destruction of the hair follicle and permanent hair loss. Treatment of cicatricial alopecia depends on the disease causing the scarring. Once the disease is resolved and only the scars remain, the bald patches can be successfully treated by simply surgically removing the bald patches if they are small, or through the use of hair transplant procedures in large patches.
Infection
Skin infections in areas of normal hair growth can result in temporary baldness. The most common causes are fungal infections (ringworm or piedra), folliculitis, microscopic parasites, or severe seborrheic dermatitis. Treatment for this form of hair loss depends on the infection causing it, but almost all can be easily treated by a dermatologist.
Other Causes
There are multitudes of congenital genetic disorders that can result in varying degrees of hair loss – ranging from the complete inability to grow hair to weak hair follicles to small patches of persistent baldness. Most are extremely rare but also difficult to treat. Finally, however, a very common cause of hair loss is not through any kind of disease or condition but by overtreatment of the hair with cosmetic products. Straightening, dyeing, bleaching, and many other popular cosmetic treatments damage hair fibers and/or hair follicles.