Folliculitis
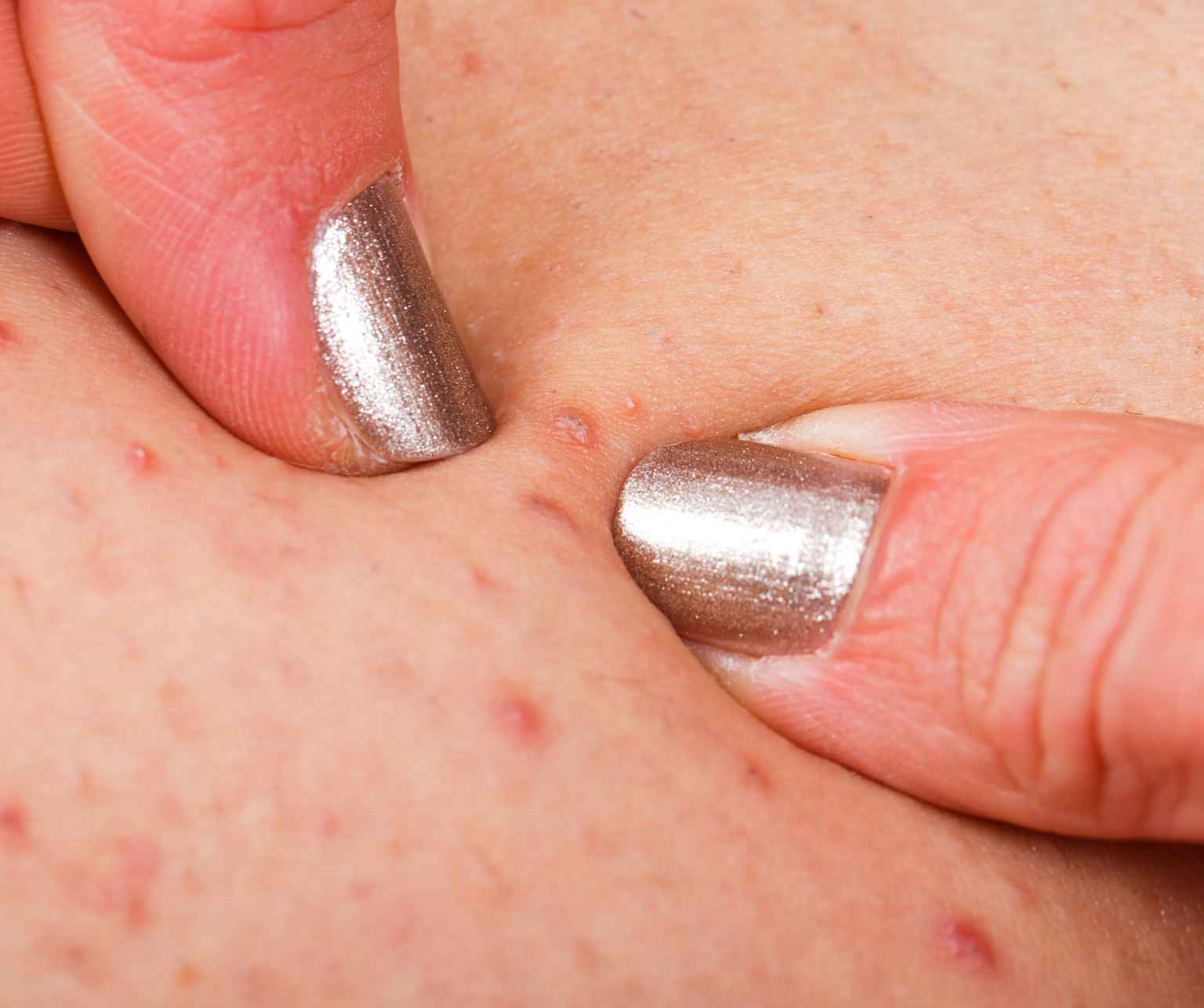
Folliculitis describes an inflamed hair follicle, usually due to a bacterial or fungal infection. It appears as red and painful bumps that have the appearance of acne. It is most common on the scalp or beard area but can occur anywhere the body has hair. Therefore, folliculitis cannot affect the palm of the hand or the sole of the foot.
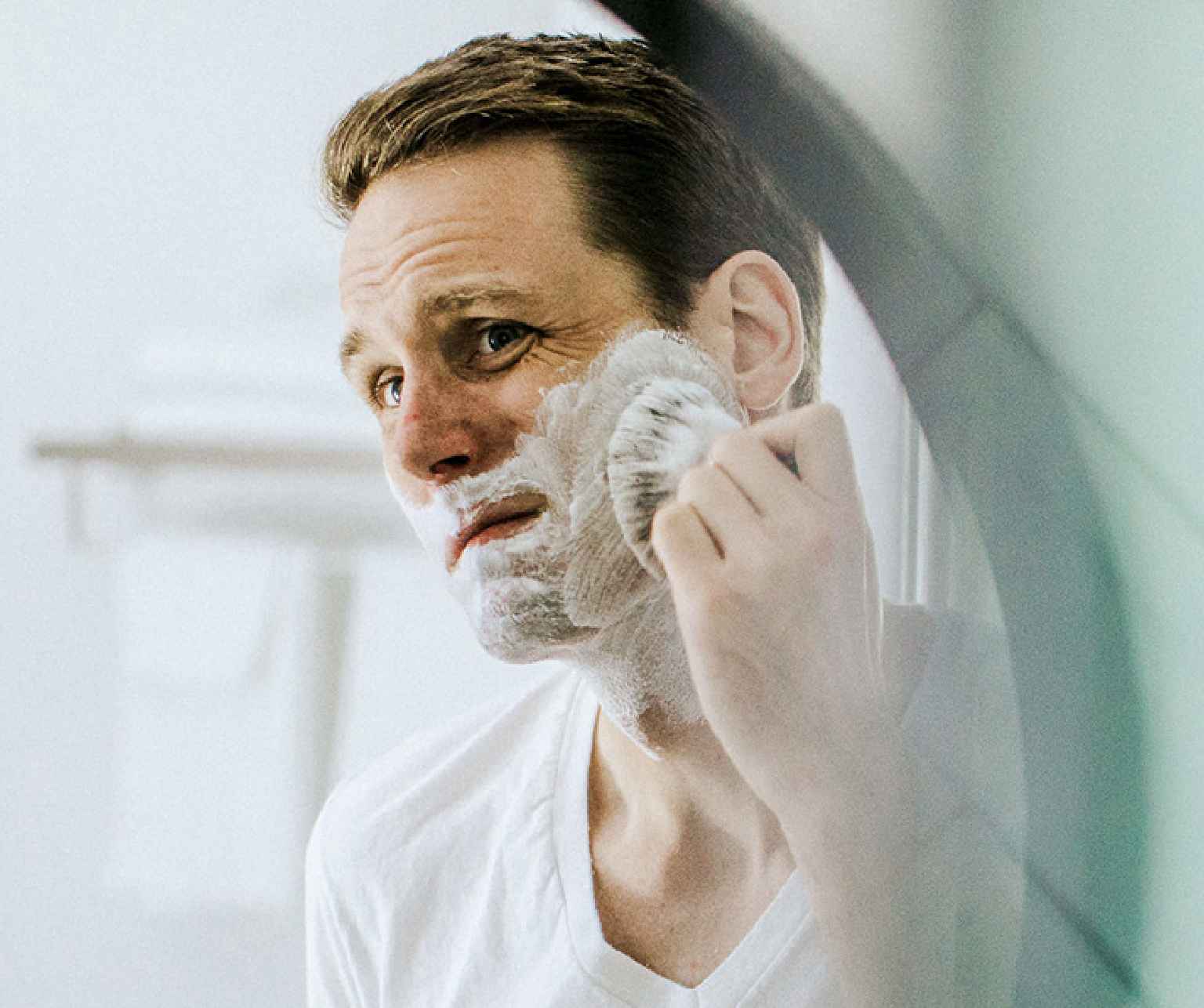
It generally occurs after a hair follicle has been damaged, making it more susceptible to infection. The most common causes of follicle damage are shaving, friction from tight clothing, exposure to heat and sweat, other conditions that irritate the skin such as acne or dermatitis, and injuries.
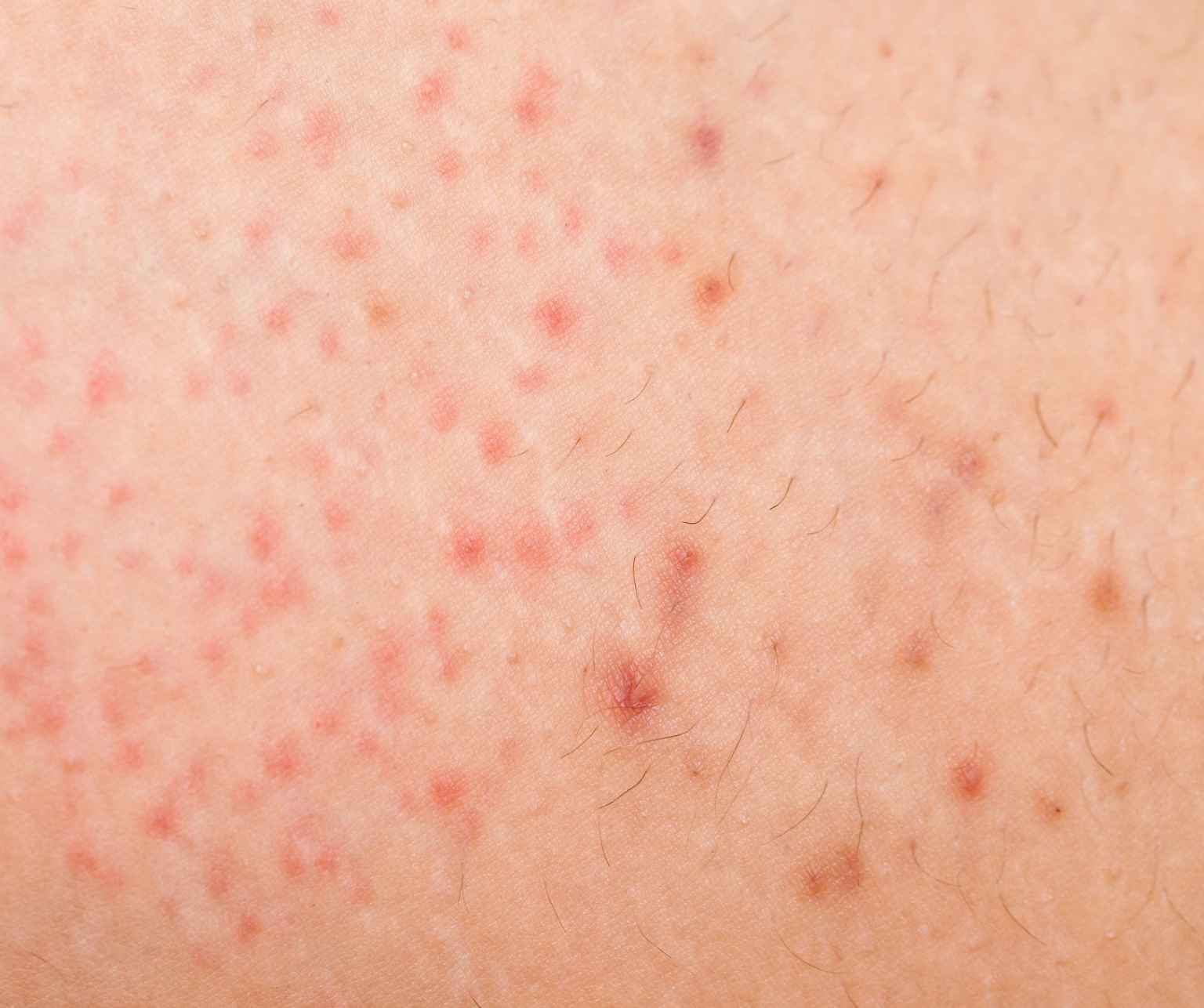
Folliculitis Can be Superficial or Deep Seated
Cases of folliculitis range from superficial, which requires no treatment, to deep, which can cause disfiguring scars and should be treated by a physician. Superficial folliculitis is most commonly caused by the bacteria staphylococcus aureus (staph), which is found normally on the skin and can only infect the follicle following a wound.
… Folliculitis can take the form of an ingrown hair without infection. This is usually caused by shaving and is known as pseudofolliculitis barbae.
It can also be caused by an infection by the pseudomonas bacteria – usually picked up through the use of dirty hot tubs and is generally worse wherever the swimsuit was touching the skin. When superficial folliculitis is due to a yeast infection it is known as pityrosporum folliculitis and usually affects the chest and back but can spread to the arms, neck, and face.
Folliculitis Can be Superficial or Deep Seated
Cases of folliculitis range from superficial, which requires no treatment, to deep, which can cause disfiguring scars and should be treated by a physician. Superficial folliculitis is most commonly caused by the bacteria staphylococcus aureus (staph), which is found normally on the skin and can only infect the follicle following a wound.
… Folliculitis can take the form of an ingrown hair without infection. This is usually caused by shaving and is known as pseudofolliculitis barbae.
It can also be caused by an infection by the pseudomonas bacteria – usually picked up through the use of dirty hot tubs and is generally worse wherever the swimsuit was touching the skin. When superficial folliculitis is due to a yeast infection it is known as pityrosporum folliculitis and usually affects the chest and back but can spread to the arms, neck, and face.
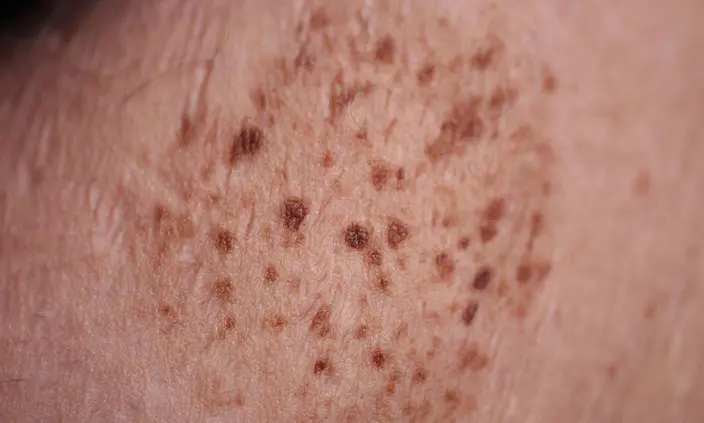
Types of Follicullitis
Finally, folliculitis can take the form of an ingrown hair without infection. This is usually caused by shaving and is known as pseudofolliculitis barbae.
If an ingrown hair becomes infected, however, it can become a deep form of folliculitis known as tinea barbae (a fungal infection) or take the form of a boil or carbuncle (a staph infection). Chronic bacterial infection of ingrown hairs in the beard area is known as Sycosis vulgaris. Deep folliculitis can also be caused by gram-negative bacteria and is usually the result of long-term antibiotic use. The antibiotics disrupt the normal balance of bacteria in the nose, leading to the proliferation of harmful gram-negative bacteria. If these bacteria spread it can cause deep folliculitis around the nose and mouth.
Folliculitis decalvans is a rare and poorly understood form of folliculitis that usually involves staph bacteria. It usually occurs in the scalp and spreads outward from a single point leaving scarring and hair loss behind. Its cause is unknown and there is no permanent cure.
Eosinophilic folliculitis is a type of deep folliculitis that affects people with HIV/AIDS. This type usually involves the scalp, face, neck, or upper chest and often causes hyperpigmentation after the inflammation dies down. No matter what type, deep folliculitis can scar and may even result in loss of hair in affected areas. Consult your physician if you believe you might have deep folliculitis.
…the best “treatment” for folliculitis is prevention. Maintain proper skin hygiene and avoid utilizing dirty hot tubs, gym equipment, and shaving razors.
Follicullitis Treatments
Normally, most treatments for folliculitis involve keeping the infected area clean and applying a topical antiseptic, antibiotic, or antifungal cream. Most cases of superficial folliculitis resolve on their own but can be helped by cleaning the area with hot soapy water, applying over-the-counter topical antibiotics and steroids, and applying pressure using a warm moist washcloth.
In severe cases an oral antibiotic may be used, minor surgery can be used to drain the lesion, or laser hair removal may be performed to prevent new cases. Prescription steroid creams may be used to reduce inflammation.
However, the best “treatment” for folliculitis is prevention. Maintain proper skin hygiene and avoid utilizing dirty hot tubs, gym equipment, and shaving razors.
Avoid anything that irritates the skin – avoid tight clothing and shave with care or avoid shaving at all, especially if you are prone to developing folliculitis. If you must shave, clean the area and apply a lubricating shaving cream 5-10 minutes before you shave to soften the hair, and apply moisturizer right after shaving.
…Consult your dermatologist if you think you have folliculitis to discuss what treatment options are best.
Folliculitis can be difficult to distinguish from acne, especially on the face. Consult your dermatologist if you think you have folliculitis to discuss what treatment options are best for you.