Raynaud's Disease
Skin Conditions
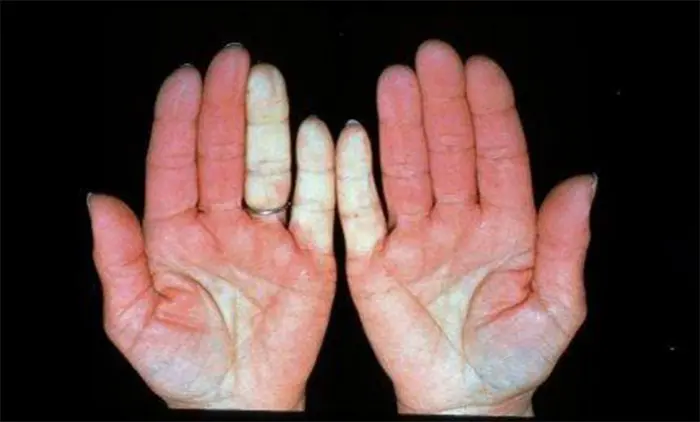
Raynaud’s disease is a condition in which the fingers (and sometimes toes, nasal tip, nipples, and earlobes) receive significantly reduced blood flow upon exposure to cold temperatures or stress. This causes the affected areas to turn cold, white, and numb and eventually blue during prolonged episodes. When blood returns to the areas they can become quite red and the affected individual may feel a “pins and needles” sensation. Raynaud’s disease occurs when vasospasms are triggered by cold or stress thus temporarily depriving the affected tissue of oxygen.
It is unknown what mechanism is causing these vasospasm to be triggered though it likely has a genetic component. Smoking tobacco and caffeine consumption increases both the severity and intensity of the attacks. In very rare severe cases this oxygen deprivation can lead to the formation of ulcers and even gangrene of the affected areas. Raynaud’s disease and Raynaud’s phenomenon are separate entities. This condition is termed Raynaud’s disease when it is not associated with a larger internal dysfunction; when it is a symptom of another disease it is known as Raynaud’s phenomenon. There is a long list of disorders associated with Raynaud’s phenomenon which is often the first or presenting symptom – preceding the other symptoms by days, months, or even years. It is associated with many connective tissue disorders such as scleroderma and lupus, eating disorders like anorexianervosa, vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, vibration white finger, Lyme disease, hypothyroidism, carpal tunnel syndrome, multiple sclerosis, magnesium deficiency, and exposure to chemicals such as mercury and vinyl chloride. Finally, certain drugs can cause Raynaud’s phenomenon including beta-blockers, some ADHD medications, migraine medications like ergotamine and sumatriptan, certain chemotherapeutic drugs, and over the counter cold medications.
Most cases of Raynaud’s disease can be easily managed by wearing warm clothing and gloves in cold weather, reducing emotional stress, and avoiding other triggers. Treatment of Raynaud’s phenomenon depends on identifying and resolving the underlying cause. In more severe cases medications may be utilized to reduce the frequency and severity of attacks. Calcium channel blockers relax and dilate capillaries which can reduce the vasospasms that leads to reduced blood flow. Alpha blockers can be used to inhibit the mechanism that causes constriction of the blood vessels and thus causing further dilation. Finally, other vasodilating medications such as nitroglycerin are helpful. If all else fails, nerve surgery can be used to block the signal causing the vasospasms. Finally, recent research has shown that botulinum toxin injections, otherwise known as Botox, can help provide relief. All cases of Raynaud’s phenomenon should be evaluation by a physician to rule out an underlying condition. Contact your physician if you are suffering from the symptoms of Raynaud’s disease for evaluation and treatment.