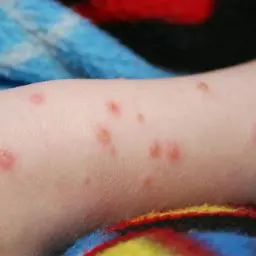
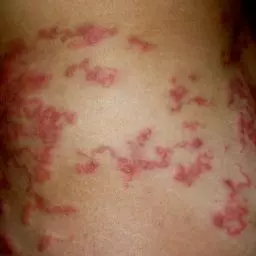
Bullous Pemphigoid
Skin Conditions
Bullous Pemphigoid is a rare chronic skin disease that causes large fluid-filled blisters that can be very itchy and if ruptured can lead to infection. While this disease occurs when the body’s immune system causes a response in the skin which causes the blisters, the reason for this response is unknown but can be linked to certain medications. This condition is most common in the >60-year-old population and can be life-threatening in this population with poor health. Common areas include the armpits, lower abdomen, and/or upper thighs.
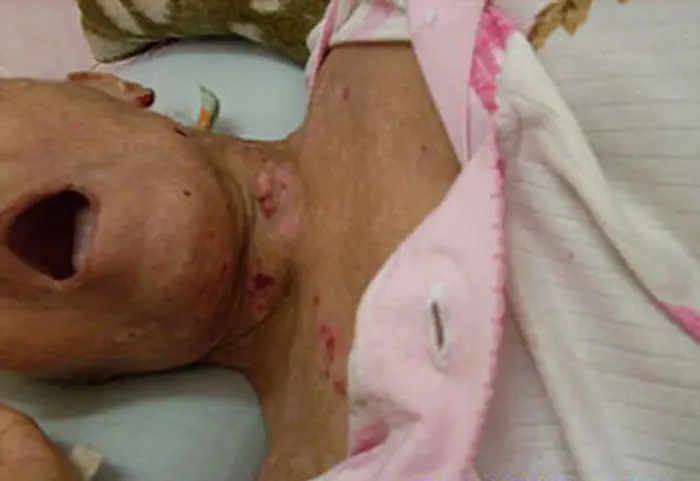
To determine if you have this condition a skin biopsy may be performed. This is when a sample lesion is selected, biopsied (excised or cut out), and then sent to a pathologist for a diagnosis. Further testing includes Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF) studies and Indirect Immunofluoresence (IDIF) studies on the biopsied lesion.
Treatment includes anti-inflammatory medication (medications that reduce or suppress inflammation) such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressant medication (medications that suppress the immune system) such as methotrexate. While this disease can be controlled some patients do require long-term treatment extending from months to years.